Disease Modeling
On this page, you'll find several resources including videos, podcasts, news articles, and academic papers related to disease modeling. Each resource includes a brief summary and recommended education level to help you decide which to click on.
Videos
Introduction to Infectious Disease Modeling

This course offers an in-depth introduction to the principles and techniques of infectious disease modeling. It covers various modeling approaches, including deterministic and stochastic models, to understand and predict the spread of infectious diseases. The course is designed for public health professionals, researchers, and college students, aiming to equip them with the essential tools to analyze disease dynamics and inform public health interventions.
Recommended Education Level: Undergraduate +
Watch VideoHow do mathematicians model infectious disease outbreaks?
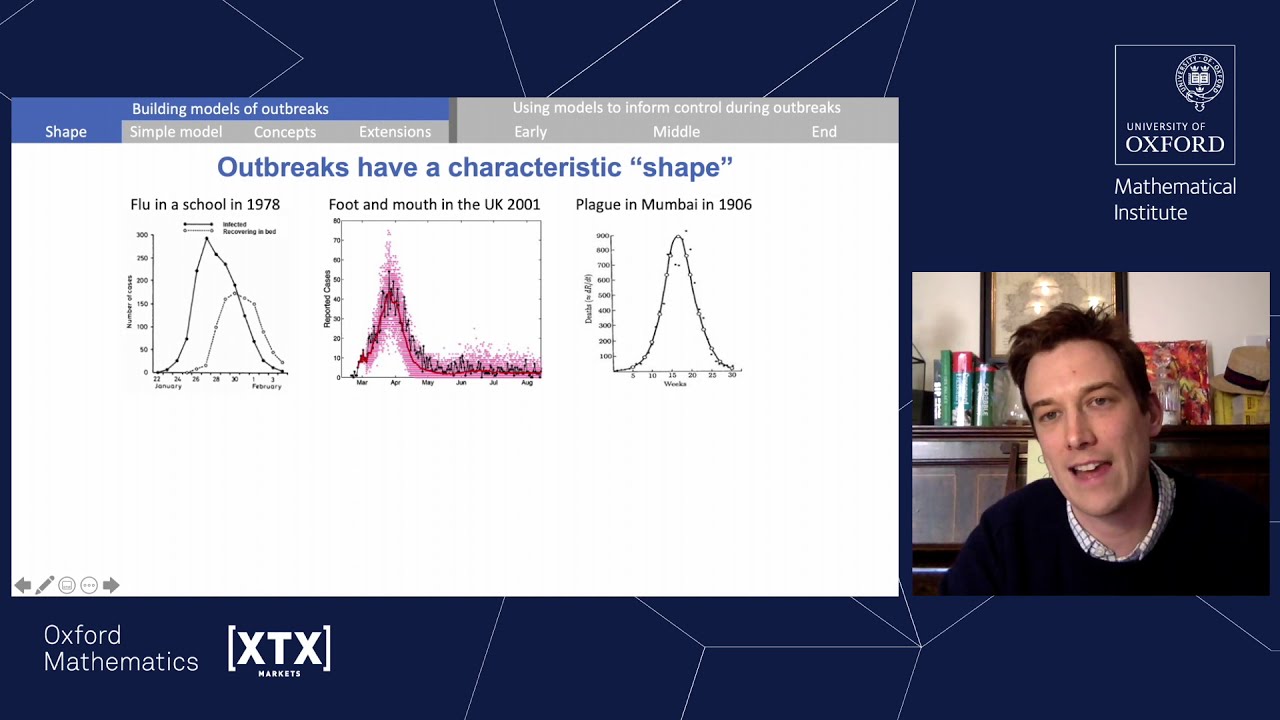
In this insightful video, the process of modeling infectious disease outbreaks is explored. The video explains how mathematicians use various mathematical models, such as the SIR (Susceptible, Infected, Recovered) model, to understand and predict the spread of diseases. It discusses the importance of parameters like transmission rates and recovery rates, and how these models can help inform public health strategies and interventions. The video aims to provide a deeper understanding of the critical role mathematics plays in epidemiology and outbreak management.
Recommended Education Level: Undergraduate +
Watch VideoArticles
The SIR Model for Spread of Disease - The Differential Equation Model
This article introduces the SIR (Susceptible, Infected, Recovered) model, a fundamental framework used to describe the spread of infectious diseases through populations. The authors explain how differential equations are used to model the dynamics of disease transmission, capturing the rates at which individuals move between the susceptible, infected, and recovered states. The article provides a mathematical foundation for understanding epidemic behavior and offers insights into predicting and controlling outbreaks.
Recommended Education Level: Undergraduate +
Read ArticleDisease Modeling: How Math Can Help In A Pandemic
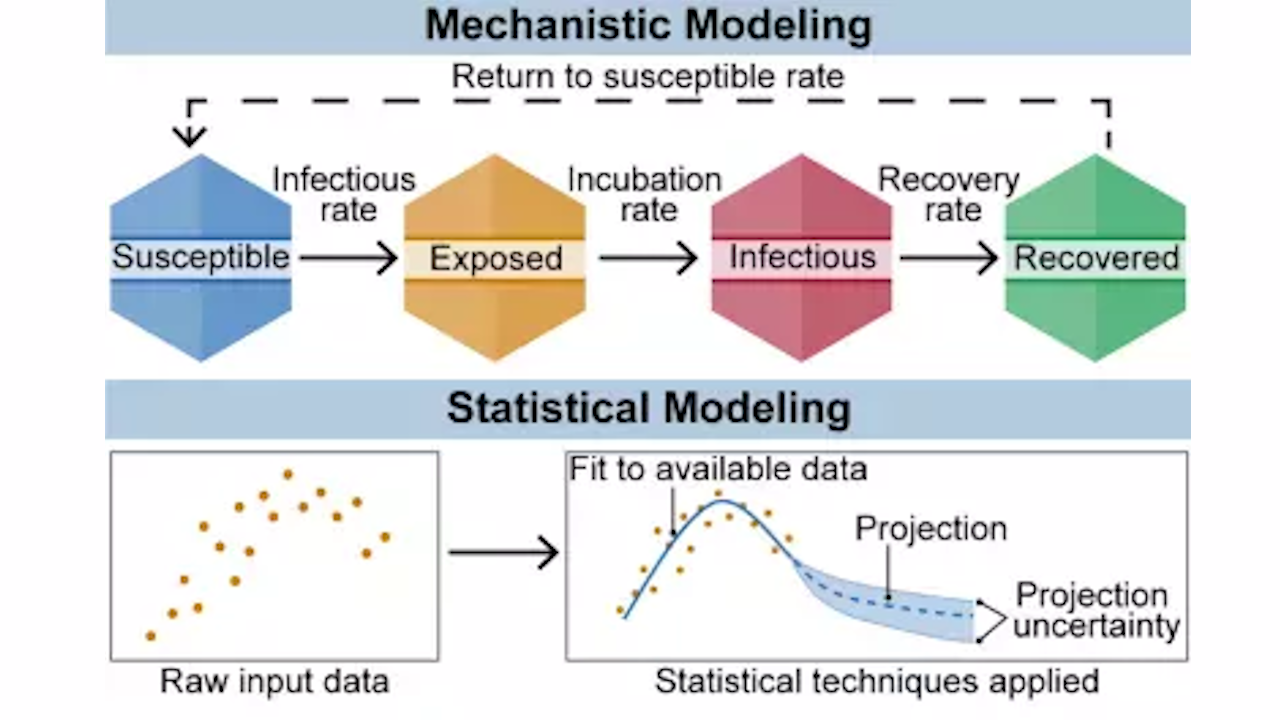
This post looks at how math models help us understand and manage pandemics. It explains how these models are used to simulate the spread of diseases, predict what might happen, and guide public health decisions. The post shows why these models are important for planning and responding to pandemics, highlighting their role in reducing the impact of outbreaks.
Recommended Education Level: Middle School +
Read ArticleAcademic Papers
Influenza Seasonality: Underlying Causes and Modeling Theories
This article examines the factors that contribute to the seasonality of influenza and reviews various theoretical models used to understand and predict its patterns. The authors explore biological, environmental, and social influences on influenza transmission and discuss how different modeling approaches can help clarify the complex dynamics of seasonal flu outbreaks.
Recommended Education Level: Undergraduate +
Read PaperPlanning horizon affects prophylactic decision-making and epidemic dynamics
This article explores the impact of different planning horizons on decision-making for prophylactic measures and the subsequent effects on epidemic dynamics. Through mathematical modeling, the authors demonstrate that shorter planning horizons can lead to less effective prophylactic decisions, potentially worsening the spread of infectious diseases. The study underscores the importance of considering long-term effects in public health planning and interventions.
Recommended Education Level: Undergraduate +
Read PaperComplexity, simplicity, and epidemiology
This article examines the balance between complexity and simplicity in the field of epidemiology. The authors discuss how complex models can provide detailed insights into disease patterns and causation, while simpler models offer clarity and ease of interpretation. They advocate for a thoughtful approach that leverages both complex and simple models to enhance understanding and address public health challenges effectively.
Recommended Education Level: High School +
Read PaperModeling the spread of infectious diseases through influence maximization
This article explores the use of influence maximization techniques to model and control the spread of infectious diseases. The authors present a framework that leverages network theory and optimization methods to identify key individuals or nodes whose influence can be maximized to effectively curb the transmission of diseases. The study provides valuable insights into designing targeted intervention strategies for epidemic control.
Recommended Education Level: Undergraduate +
Read PaperOther SEPA (Science Education Partnership Award) Projects
The Great Diseases - Infectious Diseases
"Infectious Diseases" is a unit within "The Great Diseases" curriculum module offered by Tufts University, and is aimed at teaching middle and high school students about the complexities of infectious diseases. This module covers the biology of pathogens, the mechanisms of disease transmission, the body’s defense mechanisms, and public health strategies to control infectious diseases.
Recommended Education Level: Middle School +
Visit SiteIt's Contagious! Promoting the Biomedical Workforce Pipeline through Infectious Diseases
“It's Contagious! Promoting the Biomedical Workforce Pipeline through Infectious Diseases” is an educational resource that aims to engage students in learning about infectious diseases and to inspire interest in biomedical careers. The curriculum includes interactive lessons and activities designed to enhance understanding of the science behind infectious diseases and the importance of the biomedical workforce.
Recommended Education Level: Middle School +
Visit SiteEpidemiology and the Energy Balance Equation
This educational resource offers a comprehensive curriculum focused on teaching students the principles of epidemiology, specifically in relation to energy balance, nutrition, and physical activity. It aims to deepen students' understanding of how epidemiological methods are applied to investigate the connections between lifestyle factors and health outcomes.
Recommended Education Level: Middle School +
Visit Site