Science Careers
On this page, you will find an expansive list of careers that fall under the "Science" category in STEMM. Click any career to learn more about it.
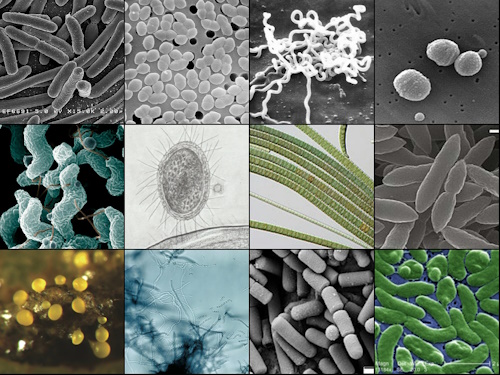
Bacteriologists focus on the study of bacteria and bacterial infections, contributing to the development of antibiotics and other treatments.
Image source: Wikipedia

Biomedical researchers conduct scientific research to advance knowledge in the field of biology and medicine. They work on developing new drugs, therapies, and medical technologies to improve health.
Image source: National Geographic

Biosecurity specialists develop and implement measures to protect against biological threats and infectious disease outbreaks, ensuring public safety and preparedness.
Image source: Wikipedia

Clinical trials managers oversee clinical trials, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and the collection of high-quality data.
Image source: Polymorphic Games Studio
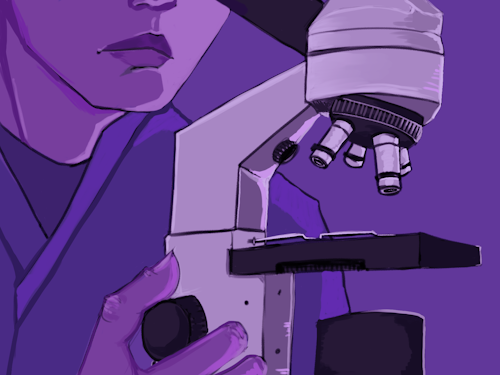
Cytotechnologists specialize in the study of cells, examining them under a microscope to detect abnormalities that may indicate diseases such as cancer. They play a crucial role in early detection and diagnosis of many diseases.
Image source: Polymorphic Games Studio

Emergency response coordinators manage public health responses to infectious disease outbreaks and other emergencies. They develop plans, coordinate resources, and provide leadership during public health crises.
Image source: Polymorphic Games Studio

Environmental health specialists investigate and control environmental factors that affect public health. They work to prevent and mitigate health risks associated with environmental hazards.
Image source: HospitalCareers

Epidemiologists study the patterns, causes, and effects of health and disease conditions in defined populations. They play a critical role in public health by investigating outbreaks, monitoring disease trends, and implementing prevention strategies.
Image source: USCOnline

Food safety specialists ensure the safety of food products to prevent foodborne illnesses, conducting inspections and developing safety protocols.
Image source: Wikipedia

Geneticists study genetic factors that influence susceptibility to diseases and develop genetic-based treatments and interventions.
Image source: Career in STEM

Global health specialists develop and implement programs, conduct research, and collaborate with international organizations to address health issues and improve healthcare outcomes worldwide.
Image source: Shemmassian Academic Consulting

Health communication specialists develop communication strategies to inform the public about health risks and promote healthy behaviors. They create materials and campaigns to distribute health information.
Image source: Grand Canyon University

Health educators teach people about behaviors that promote wellness. They develop and implement strategies to improve the health of individuals and communities.
Image source: Purdue Global
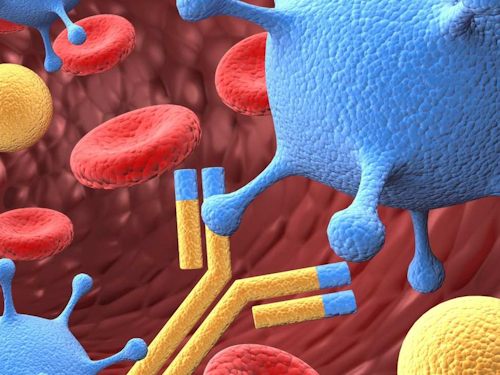
Immunologists study the immune system to understand how it defends the body against infections and diseases. They develop vaccines, treatments, and therapies to enhance immune responses.
Image source: Imperial College

Microbiologists study microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites to understand their impact on humans, animals, plants, and the environment.
Image source: CSR Wire

Occupational health specialists work to prevent and manage infectious diseases in workplace settings. They ensure that workplaces comply with health and safety regulations and promote the health of employees.
Image source: Tulane University

Parasitologists study parasites and their impact on human health and develop strategies for prevention and treatment.
Image source: St. Norbert College
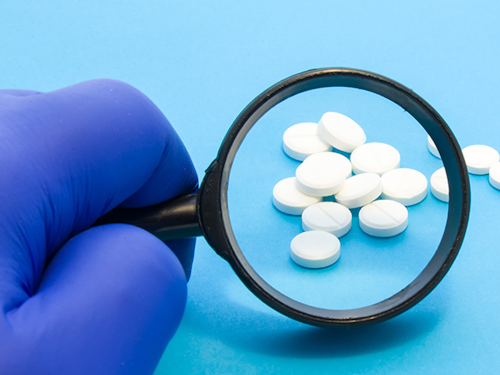
Pharmaceutical regulatory affairs specialists manage the regulatory aspects of bringing new pharmaceutical treatments to market, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
Image source: ASBMB

Public health advisors provide expertise and support for public health programs and policies. They work to improve health outcomes through program development, implementation, and evaluation.
Image source: MPHonline

Public health entomologists study insects that transmit infectious diseases, such as mosquitoes and ticks, and develop strategies to control their populations.
Image source: Indiana University Bloomington

Vaccine researchers develop and test vaccines to prevent infectious diseases. They conduct research to understand pathogens and create effective immunizations.
Image source: Penn Today
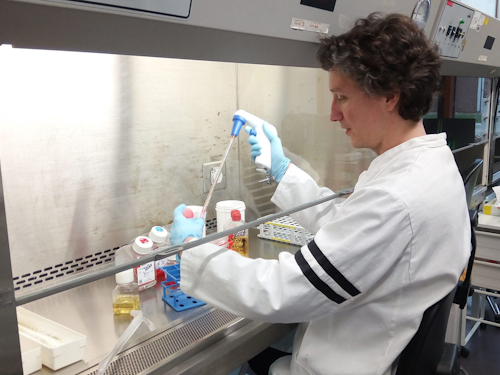
Virologists specialize in the study of viruses and viral diseases. They conduct research to understand virus behavior, develop treatments, and create vaccines.
Image source: WHO

Water quality specialists monitor and manage water quality to prevent waterborne diseases, ensuring access to safe drinking water.
Image source: Polymorphic Games Studio

Zoonotic disease specialists study diseases that can be transmitted from animals to humans. They work to understand, prevent, and control zoonotic diseases.
Image source: IAEA